Introduction: The Importance of Rebalancing
Your investment portfolio isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it plan. It shifts as markets move, and those shifts can quietly increase your risk without you realizing it. Imagine planting a balanced garden. If one plant grows too fast and takes over, it throws everything off. That’s exactly what happens when your portfolio gets out of balance. This lesson shows you:
What is Rebalancing?
Rebalancing means bringing your portfolio back to its original mix of investments. It’s how you stay in control, even when the market pulls things out of shape. Example: Let’s say your target is: After a strong year for stocks, your portfolio shifts to: Now you're taking on more risk than planned. Rebalancing means selling some stocks and buying bonds to reset back to 60/40. Why It Is Important Left alone, portfolios drift. Rebalancing brings them back in line before things get off track.
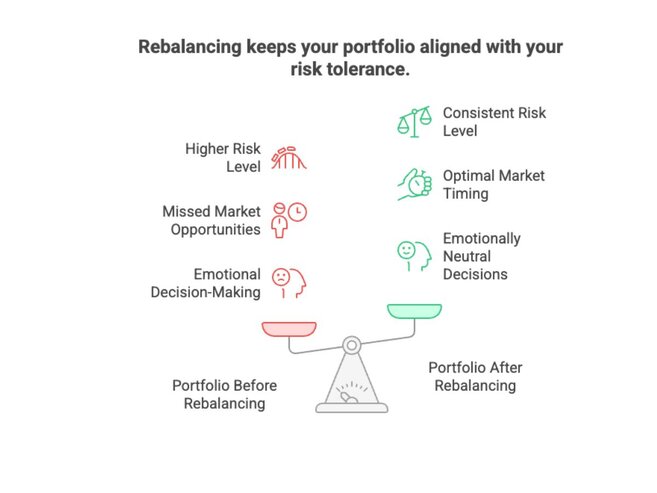
When Should You Rebalance?
There’s no one “perfect” moment to rebalance. What matters is that you do it consistently and with a plan. Here are three smart approaches: Time-Based Rebalancing Threshold-Based Rebalancing Pro tip: Don’t rebalance too often; transaction costs and taxes can eat into returns.Event-Driven Rebalancing
Managing Market Risk
You cannot control the market, but you can control how exposed you are to its ups and downs. The Role of Asset Allocation A thoughtful mix spreads out risk and smooths the ride. Know Your Comfort Zone Ask yourself: Tools to Reduce Risk Smart investing doesn’t demand risk avoidance; it demands risk management so you can stay the course.
Staying Calm During Volatility
Market dips feel scary, but they're also normal.
What matters most is how you respond.
Market Corrections vs. Crashes
- Corrections = Short-term drops of 10–20% (happen regularly)
- Crashes = Larger, more sudden declines (like 2008 or 2020)
- Both are part of investing (and both eventually pass).
Why Selling in a Panic Hurts
- When you sell in a downturn, you lock in losses
- Most investors miss the rebound, and miss out on long-term growth.
Rebalancing During a Downturn
- Falling markets may give you a chance to buy low
- Selling some bonds to buy underpriced stocks = disciplined strategy
How to Stay Steady
- Focus on your time horizon, not headlines
- Keep perspective with historical returns
- Remind yourself: volatility is the price of admission for growth
The best investors prepare for downturns, and stay invested through them.
Quiz
What does rebalancing help you do?
a) Time the market for better returns
b) Adjust your portfolio back to your target mix
c) Avoid all investment losses
When should you consider rebalancing your portfolio?
a) Every time the market moves
b) Only when you feel nervous
c) On a set schedule or when allocations drift significantly
3.What’s the biggest danger during a market downturn?
a) Not selling quickly
b) Sticking to your plan
c) Selling in a panic and locking in losses
See the answers at the bottom
Exercise: Rebalance a Sample Portfolio
You have a target allocation of:
- 60% stocks
- 30% bonds
- 10% cash
After one year, the portfolio looks like this:
- 70% stocks
- 20% bonds
- 10% cash
Questions:
- What’s out of balance?
- What would you sell? What would you buy?
- Would you rebalance now, or wait?
Summary and Key Takeaways
- Rebalancing brings your portfolio back to its original plan, keeping risk levels in check.
- Use a consistent approach: time-based, threshold-based, or triggered by big changes.
- Volatility is normal; don’t panic when markets dip.
- Staying diversified and emotionally grounded is the best defense against uncertainty.
- You can’t control the market, but you can control how you react to it.
Final thought: A steady hand beats a fast trigger. Rebalancing helps you stay on course, even when markets try to shake you off.
1) What does rebalancing help you do? Answers to the Quiz and Exercise Questions
Quiz Answers:
Answer: b) Adjust your portfolio back to your target mix
2) When should you consider rebalancing your portfolio?
Answer: c) On a set schedule or when allocations drift significantly 3) What’s the biggest danger during a market downturn? Answer: c) Selling in a panic and locking in losses
Additional resources
This section contains helpful links to related content. It isn’t required, so consider it supplemental.
-
It looks like this lesson doesn’t have any additional
resources yet. Help us expand this section by contributing
to our curriculum.
